PROJECT DESCRIPTION
The Responsive COVID-19 Vaccines for Recovery Project under the Asia-Pacific Vaccine Access Facility (APVAX) of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) provided the Government of Sri Lanka with immediate and flexible financing to implement projects activities through APVAX and from the regular country allocation. The APVAX allocation comprises of a Rapid Response Component (RRC) to support the purchase of ADB eligible coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccines, while the regular country allocation under the Project Investment Component (PIC) supports strengthening the vaccine information management system; physical infrastructure for vaccine delivery including transportation; and investments in systems for vaccine related medical waste management. Financial component of the project is $161.85 million, comprising $84 million under APVAX and $66 million from the regular country allocation, to meet the cost of vaccines for 18.2% of the population, and also to support vaccine related monitoring systems, cold chain related transport facilities, activities to ensure gender equity and inclusivity, and to strengthen medical waste management related to COVID-19 and vaccination program. The project supports the Government of Sri Lanka to ensure COVID-19 vaccine access to the population to curtail the pandemic, minimize the socioeconomic and health effects that result from it, and initiate the robust economic recovery process. The project is targeting the entire country across all 26 health districts in all nine provinces while ensuring that the geographically, socially, and economically deprived populations are protected from COVID- 19 and its effects. The beneficiary population of the project is the total population of 22 million.
EXPECTED IMPACT AND OUTCOME
The expected project impact is enhancement of the resilience and responsiveness of the health system to curtail the COVID-19 virus spread; reduce morbidity and mortality; and reduce the negative health, social, and economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic in Sri Lanka. The outcome will be priority populations of Sri Lanka vaccinated against COVID-19 as per the NDVP without compromising routine vaccine services and other health services. This outcome is to be achieved through the following four outputs.

Output 01 : COVID-19 VACCINES DELIVERED
Through the rapid response component (RRC), output 1 finances procurement of safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines to cover 18.2% of the population (4 million population). The output supports the government in reaching 80% COVID-19 vaccine coverage by 2023, with data disaggregated by sex, age, and geography. The vaccination campaign has already started following the NDVP and COVID-19 vaccination protocols.
Output 02 : VACCINATION INFORMATION DISSEMINATION AND MONITORING SYSTEMS STRENGTHENED
Through the project investment component (PIC), output 2 supports the Epidemiology Unit in the MOH to improve and enhance the electronic National Immunization Program (e-NIP) and its electronic adverse effects following immunization system under the routine vaccination program to include the COVID-19 vaccination program. This output also supports the Health Information Unit in the MOH to introduce a COVID-19 immunization tracker that will provide real-time individual beneficiary data and will help monitor the COVID-19 vaccine deployment.
Surveillance data will be shared with global and regional partners to support a collective response to the pandemic. Under the output, it is therefore intended to purchase and supply laptop computers and tablets to all medical officer of health units and provide training for managing the real-time data entry. Output 2 also supports the MSD to purchase the required consumables, supplies, and essential equipment to roll out the vaccination program as described in the NDVP. This output also provides support to the MSD to improve the logistics, regulatory capacity, and procurement capacity by enhancing the existing Medical Supplies Management Information System for managing and tracking all drugs, vaccines, and consumables in the public health system. In addition, this output supports the MSD to collaborate with the Ministry of Finance to initiate e- procurement practices in the health sector. This includes upgrading software programs, purchasing computers, establishing internet connectivity, training, and networking hospitals and related institutions. Furthermore, support is provided to the HPB of the MOH to promote gender equality and social inclusion in access to the COVID-19 vaccination. Activities include training community groups in reaching out to women and other vulnerable population groups with information on vaccinations (including specific information for pregnant and lactating women, or women with preexisting conditions and disabilities) and providing direct support to vulnerable groups to access the vaccination and related services in the respective medical officer of health areas. Output 2 also provides the management and technical support required to implement the project. This includes hiring experts for project management services like finance, procurement, engineering, information technology, and monitoring and evaluation for the project management unit (PMU) of the ongoing ADB-financed Health System Enhancement Project (HSEP).
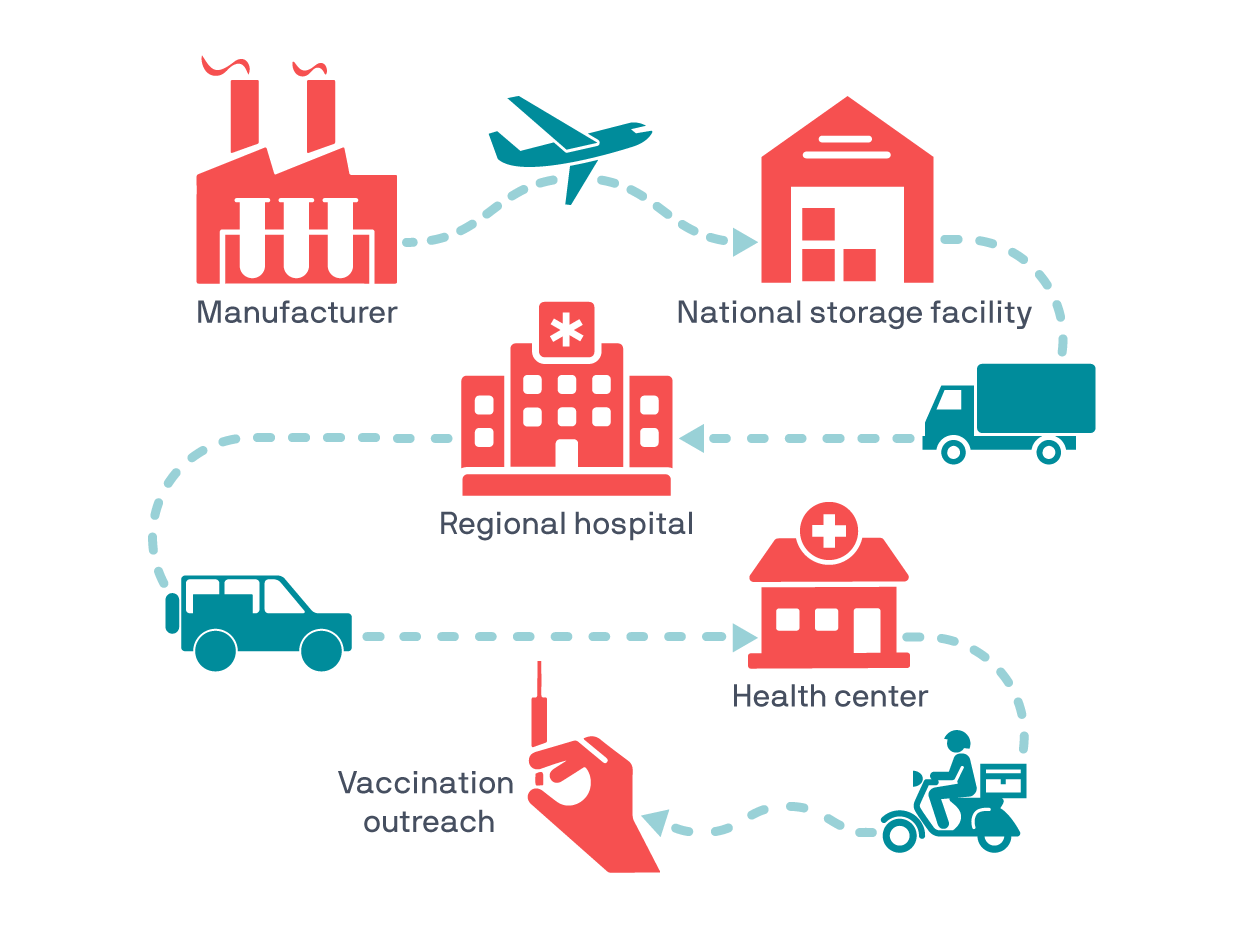
Output 03 : CAPACITY OF VACCINE TRANSPORT SYSTEMS EXPANDED
Through the PIC, output 3 supports enhancement of the capacity of the vaccine transport system from central to regional levels and the vaccine distribution system from regional drug stores to the vaccination centers. This output supports the purchase of a small refrigerated truck for each of the 26 regional drug stores and 10 large trucks for the MOH. In addition, to maintain the routine vaccination program alongside the rollout of the COVID-19 vaccination program, transport facilities are to be provided to ensure adequate human resources are mobilized for regional stores, divisional offices, vaccination centers, and regional offices for program supervision and management. This output also provides transport facilities to enable vulnerable women and people with a disability to access vaccination centers.
Output 04 : VACCINE-RELATED MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STRENGTHENED
Through the PIC, output 4 supports the implementation of the Medical Waste Management Plan of the MOH. With the expanded COVID-19 vaccination, as many as 32.0 million syringes and nearly 3.2 million vials will need to be discarded. The large number of polymerase chain reaction tests carried out (nearly 2 million) add to the volume of COVID-19 waste. In addition, with the establishment and conversion of secondary care hospitals into COVID-19 managed hospitals, many of these hospitals require well-designed sewerage management for appropriate infection prevention and control. This output supports the establishment of a sewerage system in 26 of the 87 (30%) of the secondary care hospitals in all nine provinces that require such systems.

Output 4 also supports improved medical waste management arrangements in six of the nine provinces in the country. Based on the Medical Waste Management Plan of the MOH, in the six provinces of Northern, Eastern, North Central, North Western, Uva, and Sabaragamuwa, the MOH will establish satellite waste management centers in identified secondary and tertiary care hospitals in each of the districts. This output supports the establishment of incinerators and waste segregation at 12 satellite hospitals representing the six provinces.